Original article
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Original article
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- The protective effect of CXC chemokine receptor 2 antagonist on experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia induced by postnatal systemic inflammation
- Seung Hyun Lee, Chang Won Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):37-43. Published online July 15, 2020
-

Question: Can CXC chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) antagonist preserve alveolarization by attenuating the inflammation induced by systemic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration in a rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)?
Finding: CXCR2 antagonist significantly decreased neutrophil counts in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood induced by systemic LPS administration and restored alveolarization in newborn rats.
Meaning: CXCR2 antagonist protected the lungs from the inflammation in a rat model of BPD.
- Gastroenterology
- Noninvasive markers for esophageal varices in children with cirrhosis
- Parisa Rahmani, Fatemeh Farahmand, Ghobad Heidari, Azadeh Sayarifard
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):31-36. Published online July 21, 2020
-
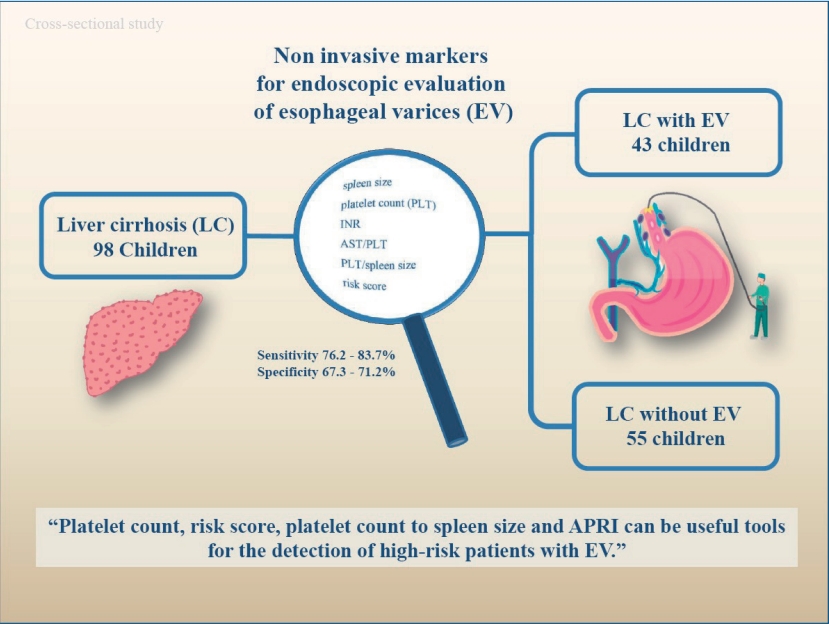
Question: Can noninvasive biomarkers identify esophageal varices among children with esophageal cirrhosis?
Finding: The spleen size, platelet count, international normalized ratio, aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index, platelet count to spleen size ratio, and risk score differed significantly between the patients with and those without esophageal varices.
Meaning: These biological parameters can predict esophageal varices among pediatric patients and indicate the need for esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Sonographic renal length and volume of normal Thai children versus their Chinese and Western counterparts
- Chantima Rongviriyapanich, Thanarat Sakunchit, Chirawat Sudla, Supamas Mungkung, Napapong Pongnapang, Chai Hong Yeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):491-498. Published online July 13, 2020
-
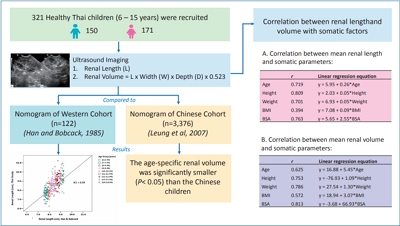
Question: What is the normal renal size of Thai children and is the renal nomogram comparable to those of Western and Chinese cohorts?
Finding: The renal length of Thai children was moderately correlated with that of Western children, while the age-specific renal volume was significantly smaller than that of Chinese children.
Meaning: Renal size in children can vary among regions and sociodemographic backgrounds; hence, a local reference standard is needed.
- Gastroenterology
- Evaluating the effects of probiotics in pediatrics with recurrent abdominal pain
- Parisa Rahmani, Azin Ghouran-orimi, Farzaneh Motamed, Alireza Moradzadeh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):485-490. Published online July 21, 2020
-
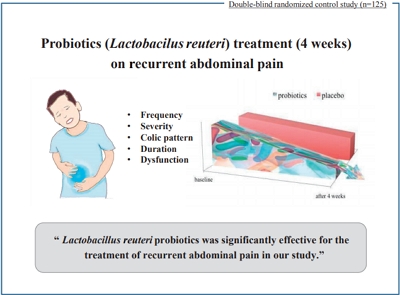
Question: ecurrent abdominal pain (RAP) is a chief complaint among pediatrics and is associated with reduced quality of life, for both parent and child, and economic burden. Does probiotics reduce the frequency of RAP among children?
Finding: This study reported the effects of Lactobacillus reuteri probiotics among children with RAP as a result of multiple etiologies.
Meaning: The administration of probiotic supplements is significantly associated with pain relief among RAP children presented with functional abdominal pain, irritable bowel syndrome, and functional dyspepsia.
- Acquired noncaustic esophageal strictures in children
- Elif Sag, Aysenur Bahadir, Mustafa Imamoglu, Sefa Sag, Gokce Pinar Reis, Erol Erduran, Murat Cakir
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):447-450. Published online October 15, 2020
-
Question: Which clinical findings suggest esophageal structure in children with dysphagia?
Finding: The presence of solid dysphagia, malnutrition, and a comorbid condition is suggestive of esophageal stricture in children with dysphagia.
Meaning: Patients with findings suggestive of noncaustic esophageal stricture should receive early referral to pediatric gastroenterology units.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Development of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST)
- Hee Jung Chung, Donghwa Yang, Gun-Ha Kim, Sung Koo Kim, Seoung Woo Kim, Young Key Kim, Young Ah Kim, Joon Sik Kim, Jin Kyung Kim, Cheongtag Kim, In-Kyung Sung, Son Moon Shin, Kyung Ja Oh, Hee-Jeong Yoo, Hee Joon Yu, Seoung-Joon Lim, Jeehun Lee, Hae-Ik Jeong, Jieun Choi, Jeong-Yi Kwon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):438-446. Published online May 14, 2020
-
Question: Can the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) be a useful screening tool for infants and children in Korea?
Finding: The K-DST has high reliability (internal consistency of 0.73–0.93, test-retest reliability of 0.77–0.88) and a high discriminatory ability with a sensitivity of 0.833 and specificity of 0.979.
Meaning: The K-DST is an effective and reliable screening tool for infants and children with neurodevelopmental disorders in Korea.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Knowledge and perceptions of kangaroo mother care among health providers: a qualitative study
- Hadi Pratomo, Tiara Amelia, Fatmawati Nurlin, Asri C. Adisasmita
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):433-437. Published online July 21, 2020
-

Question: What are health providers’ knowledge and perceptions of Kangaroo mother care (KMC)?
Finding: Health providers’ knowledge of KMC was sufficient; however, some of their perceptions about it could create barriers to the successful implementation of hospital KMC programs.
Meaning: Health providers’ perceptions about KMC should be considered to ensure successful KMC implementation. Locally designed on-site training programs could overcome the challenges.
- Risk-based maternal group B Streptococcus screening strategy is compatible with the implementation of neonatal early-onset sepsis calculator
- Niek B. Achten, J. Wendelien Dorigo-Zetsma, Annemarie M.C. van Rossum, Rianne Oostenbrink, Frans B. Plötz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):406-410. Published online April 16, 2020
-
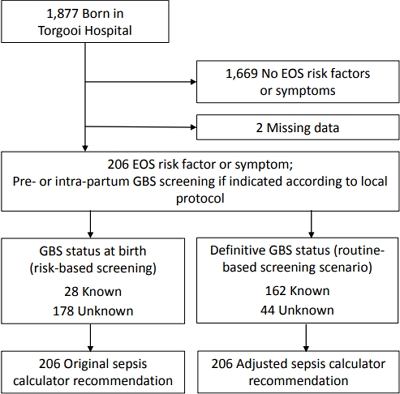
Question: To what extent does risk-based Group B Streptococcus (GBS) screening influence management recommendations by the early-onset sepsis (EOS) calculator?
Finding: In 97% of the newborn infants, the EOS calculator recommendation remained unchanged after the GBS status at birth was updated to the definitive GBS status.
Meaning: Risk-based GBS screening results are compatible with EOS calculator recommendations.
- Endocrinology
- Zinc transporter 8 autoantibody in the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in children
- Nur Rochmah, Muhammad Faizi, Siti Wahyu Windarti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):402-405. Published online October 6, 2020
-
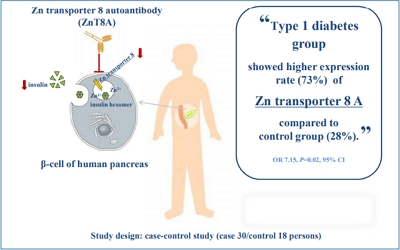
Question: Can zinc transporter 8 autoantibody (ZnT8A) be used for diagnosing type 1 diabetes (T1D)?
Finding: Twenty-two of 30 subjects with type 1 diabetes (73.3 %) were positive for ZnT8A compared to 5 of 18 controls (27.8%).
Meaning: ZnT8A has potential for clinical applications in the diagnosis of T1D.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- New modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery category and mortality in premature infants with critical congenital heart disease
- Young Mi Yoon, Seong Phil Bae, Yoon-Joo Kim, Jae Gun Kwak, Woong-Han Kim, Mi Kyoung Song, Seung Han Shin, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):395-401. Published online July 15, 2020
-
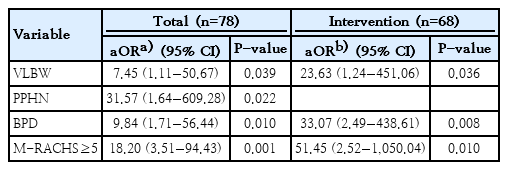
Questions: This study aimed to describe the survival of premature infants with critical congenital heart disease (CHD) and to identify the risk factors including the new modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery (M-RACHS) associated with mortality.
Finding: For premature infants with critical CHD, survival rate was 76.9% and very low birth weight (VLBW), persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), and M-RACHS 5 or more were associated with in-hospital mortality.
Meaning: VLBW, PPHN and BPD, as well as M-RACHS≥5, were risk factors for mortality among premature infants with critical CHD.
- Neurobehavior
- Association between assisted reproductive technology and autism spectrum disorders in Iran: a case-control study
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Mahdieh Seyedi, Ronak Hamzehei, Saeid Bashirian, Mohammad Rezaei, Katayoon Razjouyan, Salman Khazaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):368-372. Published online March 27, 2020
-

Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder defined by impairments in social interaction and verbal and nonverbal communication.
Purpose: Determine the association between use of assisted reproduction technology (ART) and the risk of ASD among children. Methods: This case-control study included 300 participants (100 cases, 200 controls). The control group included women with a child aged 2–10 years without ASD,...
- Other
- Evaluation of goodness of fit of semiparametric and parametric models in analysis of factors associated with length of stay in neonatal intensive care unit
- Fatemeh Kheiry, Sadegh Kargarian-Marvasti, Sima Afrashteh, Abolfazl Mohammadbeigi, Nima Daneshi, Salma Naderi, Seyed Hossein Saadat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):361-367. Published online June 10, 2020
-

Question: Hospitalization in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is associated with life-threatening hazards. What factors associated with neonatal length of stay (LOS) in the NICU?
Finding: Breastfeeding, phototherapy, acute renal failure (ARF), mechanical ventilation, and central venous catheter (CVC) access were identified as factors associated with NICU length of stay.
Meaning: Protective effects of breastfeeding and CVC access, whereas increase effects of phototherapy, ARF, and mechanical ventilation in LOS can be supporting evidence to establish effective interventions to reduce length of NICU stay.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of the role of ischemia modified albumin in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Mohamed A. Talat, Rabab M. Saleh, Mohammed M. Shehab, Naglaa A. Khalifa, Maha Mahmoud Hamed Sakr, Walaa M. Elmesalamy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):329-334. Published online August 15, 2020
-
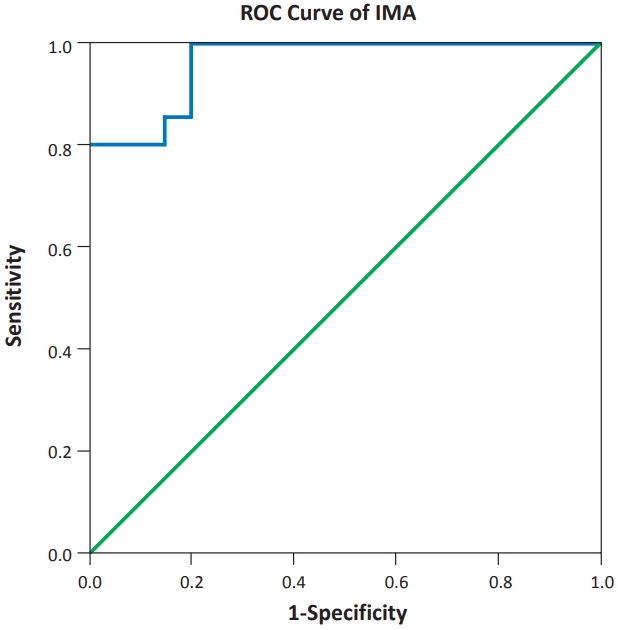
Question: What is the value of ischemia modified albumin (IMA) as a diagnostic marker for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)?
Finding: IMA levels were significantly higher (nearly double elevation) in hypoxic than healthy newborns in the first few hours after birth in the full-term neonates.
Meaning: IMA can be a reliable marker for the early diagnosis of neonatal HIE and can be a predictor of injury severity.
- Cardiology
- Age-, sex-, and height-based blood pressure reference charts, Yazd children 6–18 years, Iran
- Nastaran ahmadi, Seyedeh Mahdieh Namayandeh, Seyed Mahmood Sadr Bafghi, Mohammad Reza Mohammadi, Masoud Mirzaei, Mohammadtaghi Sarebanhassanabadi, Amir Houshang Mehrparvar, Reza Faraji, Neda Nilforoshan, Ahmad Karimi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):321-328. Published online July 21, 2020
-
Question: What is the 90th, 95th, 99th percentile of blood pressure based on height as the cut point for diagnosis of hypertension in children of our province?
Finding: We used blood pressure of 456 males and 579 females in 6–18 years old in “Iranian Children and Adolescents' Psychiatric Disorders survey.
Meaning: The 90th, 95th, 99th percentiles of systolic and diastolic blood pressure in both sex based on age and 10-cm height intervals were developed in Yazd.
- Hematology
- Effects of α-tocopherol on hemolysis and oxidative stress markers on red blood cells in β-thalassemia major
- Nora Sovira, Munar Lubis, Pustika Amalia Wahidiyat, Franciscus D. Suyatna, Djajadiman Gatot, Saptawati Bardosono, Mohammad Sadikin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):314-320. Published online August 15, 2020
-

Question: Is the α-tocopherol as an exogenous antioxidant supplementation effective in improving hemolysis and oxidative stress on β-thalassemia major?
Finding: We found significant enhancements in plasma haptoglobin were noted in the α-tocopherol group (3.01 mg/dL; range, 0.60–42.42 mg/dL; P=0.021).
Meaning: The α-tocopherol can improve hemolysis by increasing the haptoglobin level as hemolysis marker.
- Allergy
- Ten-year trends and prevalence of asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis among the Korean population, 2008–2017
- Jihyun Ha, Seung Won Lee, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):278-283. Published online January 29, 2020
-
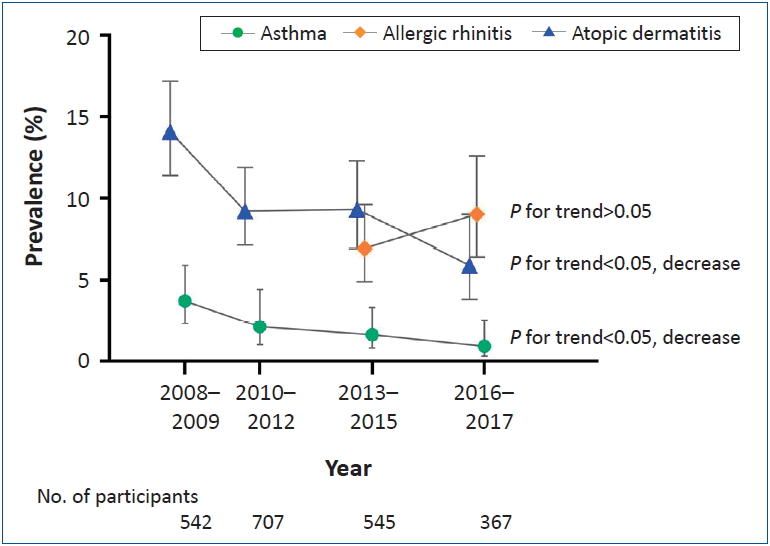
Background: Major questions remain regarding the agestratified trends of allergic diseases and asthma in Korea.
Purpose: To identify the estimated recent prevalence and 10- year trends in asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis among the Korean population from 2008 to 2017. Methods: This nationwide cross-sectional survey (Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey) over 10 years (2008–2017) examined representative samples of the...
- General Pediatrics
- Efficacy of conservative treatment of perianal abscesses in children and predictors for therapeutic failure
- Lars Boenicke, Johannes Doerner, Stefan Wirth, Hubert Zirngibl, Mike Ralf Langenbach
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):272-277. Published online May 15, 2020
-
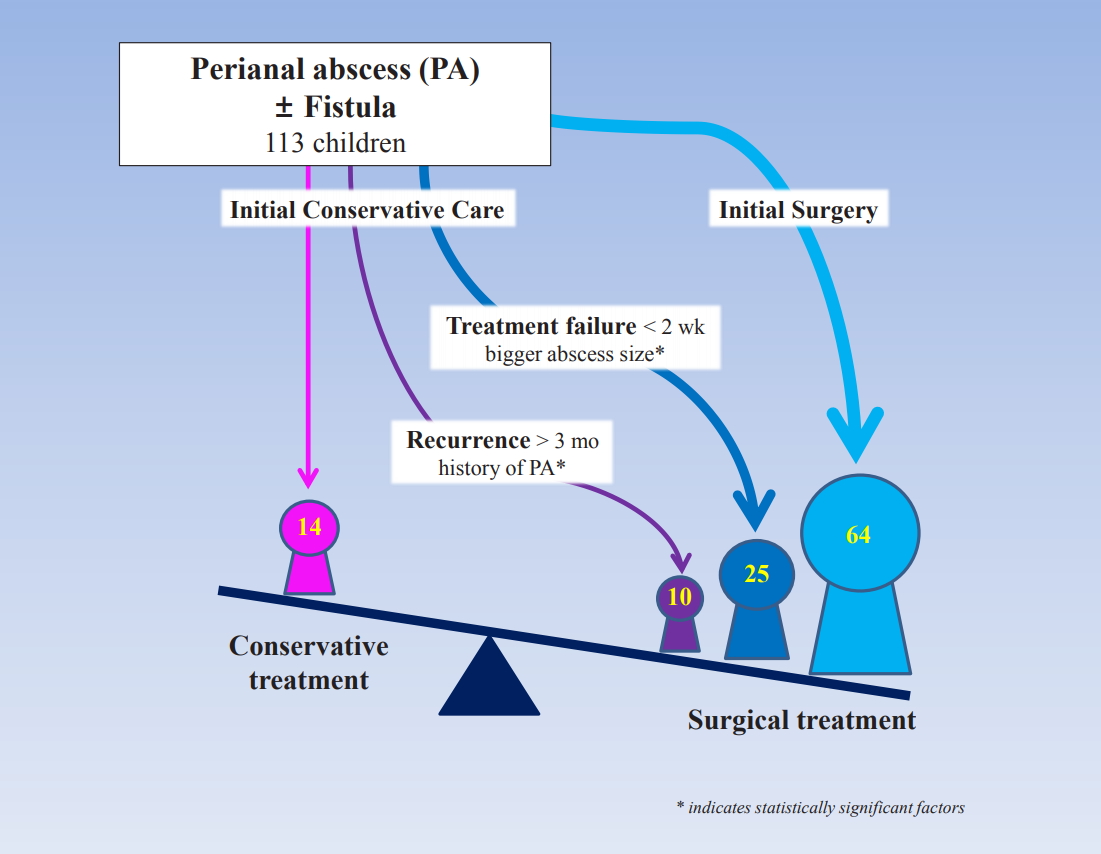
Background: The optimal management of perianal abscess in children is controversial.
Purpose: To evaluate the efficiency of conservative treatment of perianal abscess in children and identify parameters that predict therapy failure. Methods: All cases of children younger than 14 years of age with perianal abscesses between 2001–2016 were evaluated. Results: Of the 113 enrolled patients, 64 underwent subsequent surgery for advanced disease (primary...
- Immunology
- Immunogenicity and safety of a 12-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in infants aged 6–10 weeks: a randomized double-blind active-controlled trial
- Jonghoon Shin, Jamaree Teeratakulpisarn, Thanyawee Puthanakit, Tuangtip Theerawit, Ji Hwa Ryu, Jinhwan Shin, Seulgi Lee, Hayoung Lee, Kyungjun An, Hun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):265-271. Published online December 6, 2019
-
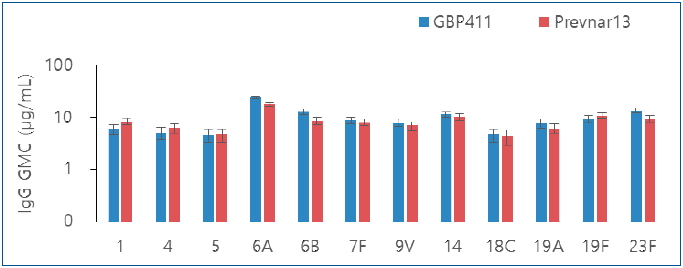
Question: The immunogenicity and safety of GBP411 when administered to healthy infants are not understood.
Finding: The intergroup differences were not significant for all 12 serotypes after the booster dose. The overall incidence of solicited local adverse events between the groups did not differ significantly.
Meaning: GBP411 with a 2p+1 dosing schedule induced a substantial immune response, and may be safe for administration to healthy infants.
- General Pediatrics
- Ability of children to perform touchscreen gestures and follow prompting techniques when using mobile apps
- Savita Yadav, Pinaki Chakraborty, Arshia Kaul, Pooja, Bhavya Gupta, Anchal Garg
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):232-236. Published online February 5, 2020
-

Background: Children today get access to smartphones at an early age. However, their ability to use mobile apps has not yet been studied in detail.
Purpose: This study aimed to assess the ability of children aged 2–8 years to perform touchscreen gestures and follow prompting techniques, i.e., ways apps provide instructions on how to use them. Methods: We developed one mobile app...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Synbiotics use for preventing sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight neonates: a randomized controlled trial
- Ozge Serce Pehlevan, Derya Benzer, Tugba Gursoy, Guner Karatekin, Fahri Ovali
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):226-231. Published online February 5, 2020
-
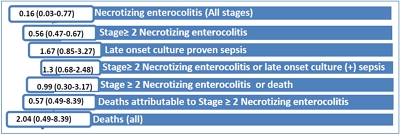
Background: Probiotics and prebiotics have strain-specific effects on the host. Synbiotics, a mixture of probiotics and prebiotics, are proposed to have more beneficial effects on the host than either agent has alone.
Purpose: We performed a randomized controlled trial to investigate the effect of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium together with oligosaccharides and lactoferrin on the development of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) or sepsis...
- Long-term cognitive, executive, and behavioral outcomes of moderate and late preterm at school age
- Ju Hyun Jin, Shin Won Yoon, Jungeun Song, Seong Woo Kim, Hee Jung Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):219-225. Published online September 25, 2019
-
Question: Infants born at moderate to late preterm gestations are known to have little problem later on, but is that really true?
Finding: At school age, cognitive problem was observed in about a quarter of the children. In addition, more than half of the children was suspected of having attention problems.
Meaning: Moderate to late preterm infants are at risk of developing abnormal intelligence and attention problems at early school age, therefore they should not be neglected on longterm follow-up evaluation.
- Cardiology
- Importance of pulmonary valve morphology for pulmonary valve preservation in tetralogy of Fallot surgery: comparison of the echocardiographic parameters
- Su Jin Choi, Jung Eun Kwon, Da Eun Roh, Myung Chul Hyun, Hanna Jung, Young Ok Lee, Joon Yong Cho, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(5):189-194. Published online November 8, 2019
-

Question: Is echocardiographic examination is useful for surgical method decision in patients with tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)?
Finding: Various echocardiographic parameters serve as predictors for determining surgical methods for TOF patients. However, the PV morphology and tissue characteristics should also be considered.
Meaning: A full dependence on the size of the pulmonary valve annulus (PVA), the z score, and the ratio of the size of PVA to aortic valve annulus or descending aorta surgery may result in inadequate surgical results during TOF total correction.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Assessment of interhospital transport care for pediatric patients
- Krittiya Chaichotjinda, Marut Chantra, Uthen Pandee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(5):184-188. Published online August 29, 2019
-

Background: Many critically ill patients require transfer to a higher-level hospital for complex medical care. Despite the publication of the American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines for pediatric interhospital transportation services and the establishment of many pediatric transport programs, adverse events during pediatric transport still occur.
Purpose: To determine the incidence of adverse events occurring during pediatric transport and explore their complications...
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Variation in clinical usefulness of biomarkers of acute kidney injury in young children undergoing cardiac surgery
- Hee Sun Baek, Youngok Lee, Hea Min Jang, Joonyong Cho, Myung Chul Hyun, Yeo Hyang Kim, Su-Kyeong Hwang, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):151-156. Published online February 5, 2020
-
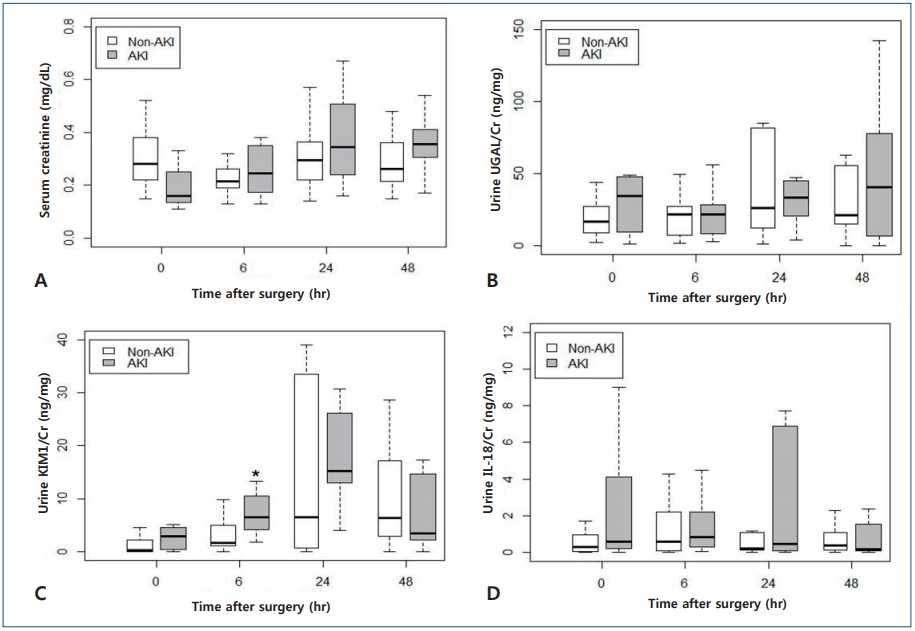
Question: Can clinical usefulness of biomarkers of acute kidney injury vary on the clinical circumstances?
Finding: In young children undergoing cardiac surgery, urine KIM-1/Cr level peaked at 24 hours with significant difference from baseline level and was significantly higher at 6 hours in the AKI group. However, urine NGAL/Cr and IL-18/Cr levels showed no specific trend with time for 48 hours after cardiac surgery.
Meaning: Urine KIM-1/Cr concentration could be considered a good biomarker for early AKI prediction after open cardiac surgery in young children.
- Endocrinology
- Effect of agricultural pesticide on precocious puberty in urban children: an exploratory study
- Junghwan Suh, Han Saem Choi, Ahreum Kwon, Hyun Wook Chae, Ho-Seong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):146-150. Published online December 6, 2019
-
Question: Does agricultural pesticide effect precocious puberty in girls?
Finding: Dinotefuran, an insecticide of neonicotinoid class, was detected in one of 30 patients with precocious puberty, and in 2 girls of the normal control group, which was not statistically significant.
Meaning: There was no close relationship between agricultural pesticides and development of precocious puberty.
- Other
- Korean parents’ perceptions of the challenges and needs on school re-entry during or after childhood and adolescent cancer: a multi-institutional survey by Korean Society of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology
- Jun Ah Lee, Jae Min Lee, Hyeon Jin Park, Meerim Park, Byung Kiu Park, Hee Young Ju, Ji Yoon Kim, Sang Kyu Park, Young Ho Lee, Ye Jee Shim, Heung Sik Kim, Kyung Duk Park, Yeon-Jung Lim, Hee Won Chueh, Ji Kyoung Park, Soon Ki Kim, Hyoung Soo Choi, Hyo Seop Ahn, Jeong Ok Hah, Hyoung Jin Kang, Hee Young Shin, Mee Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):141-145. Published online November 14, 2019
-
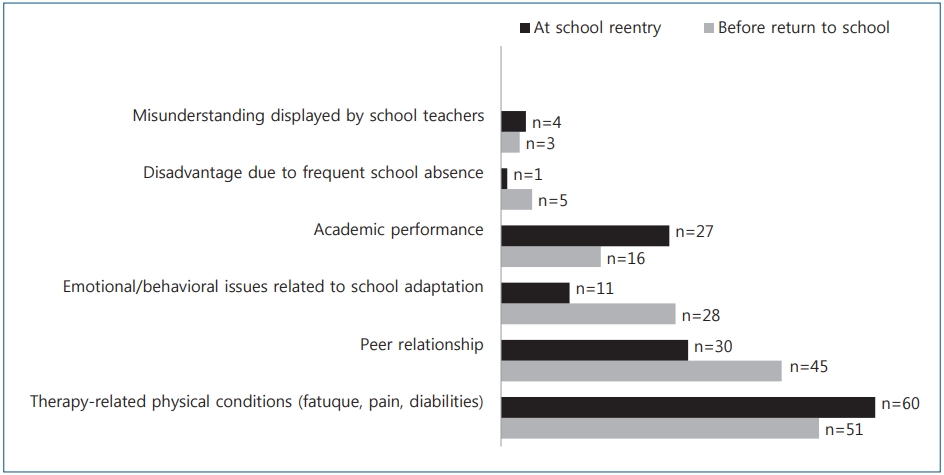
Question: What are the parental needs and challenges when their children return to school after cancer?
Finding: In addition to scholastic aptitude-oriented programs, emotional and psychosocial support is necessary for a successful return to school.
Meaning: Pediatric oncologists should actively engage in improving oncology practices to better integrate individualized school plans and educate peers and teachers to improve health literacy to make them understand the needs of children with cancer.
- Nutrition
- Positive association of breastfeeding on respiratory syncytial virus infection in hospitalized infants: a multicenter retrospective study
- Min Jeong Jang, Yong Joo Kim, Shinhye Hong, Jaeyoon Na, Jong Hee Hwang, Son Moon Shin, Young Min Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):135-140. Published online November 12, 2019
-
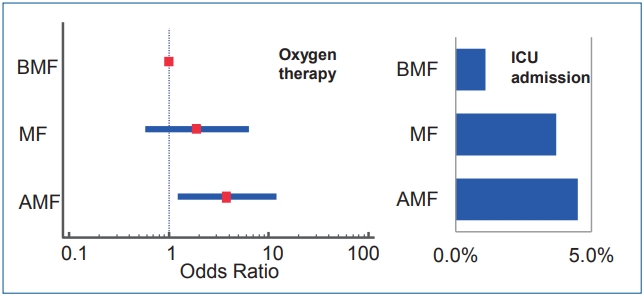
Question: Human milk has stronger antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties compared with formula milk. How dose breastfeeding affect respiratory syncytial virus infection in Korea?
Finding: Breastfed infants required less oxygen therapy and possible intensive care unit admission than artificial formulafed infants during respiratory syncytial virus infection.
Meaning: This protective role of breast milk on RSV severity can be a supporting evidence for promoting breastfeeding in Korea.
- Endocrinology
- Influence of subclinical hypothyroidism on metabolic parameters in obese children and adolescents
- Ozlem Kara
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):110-114. Published online March 6, 2020
-

Question: Does subclinical hypothyroidism in obese children and adolescents affect metabolic parameters?
Finding: Insulin, HOMA-IR, and TG levels were higher and the HDL-C level was lower in patients with SH.
Meaning: A clear association is observed between SH, and insulin resistance and dyslipidemia in obese children. It can be said that the TSH may be evaluated as a metabolic risk factor in obese patients.
- Allergy
- Asthma predictive index as a useful diagnostic tool in preschool children: a cross-sectional study in Korea
- Dong Hyeon Lee, Ji-Won Kwon, Hyung Young Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Hyo-Bin Kim, So-Yeon Lee, Gwang-Cheon Jang, Dae-Jin Song, Woo Kyung Kim, Young-Ho Jung, Soo-Jong Hong, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):104-109. Published online November 8, 2019
-

Question: Is physician-diagnosed current asthma in preschool children associated with the asthma predictive index, atopic sensitization, or pulmonary function test?
Finding: Physician-diagnosed current asthma in preschool children was associated with the asthma predictive index, but not with spirometry, methacholine provocation test, fractional expiratory nitric oxide level, and atopic sensitization.
Meaning: Physician-diagnosed asthma in preschool children may be different from classic atopic asthma in school children or adolescents.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of red blood cell transfusion on short-term outcomes in very low birth weight infants
- Eui Young Lee, Sung Shin Kim, Ga Young Park, Sun Hyang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):56-62. Published online February 6, 2020
-
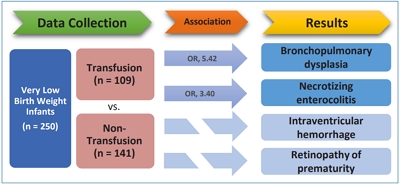
Question: Does RBC transfusion affect the short-term outcomes of VLBW infants?
Finding: The results showed that RBC transfusion was significantly related to the incidence of BPD (OR, 5.42; P<0.001) and NEC (OR, 3.40; P=0.009).
Meaning: Careful consideration of the patient’s clinical condition and appropriate guidelines is required before administering RBC transfusions.
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







